Small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) released by the cells mediate cell-to-cell communication, playing important roles in physiological and pathological contexts. Also, they are attracting attention as highly biocompatible delivery vesicles, so methods to control their production are of great interest. Despite the importance of sEV release processes, a comprehensive understanding of their regulation has remained elusive due to the lack of high-throughput methods for the comprehensive analysis of the complex sEV release processes.
Thus, the HFSP Career Development Awardee Ryosuke Kojima, from the University of Tokyo, and team, developed a new high-throughput assay platform for sEV release processes, named "CIBER screening", that uses sEVs barcoded with guide RNA (gRNA) of the CRISPR Cas9 system.
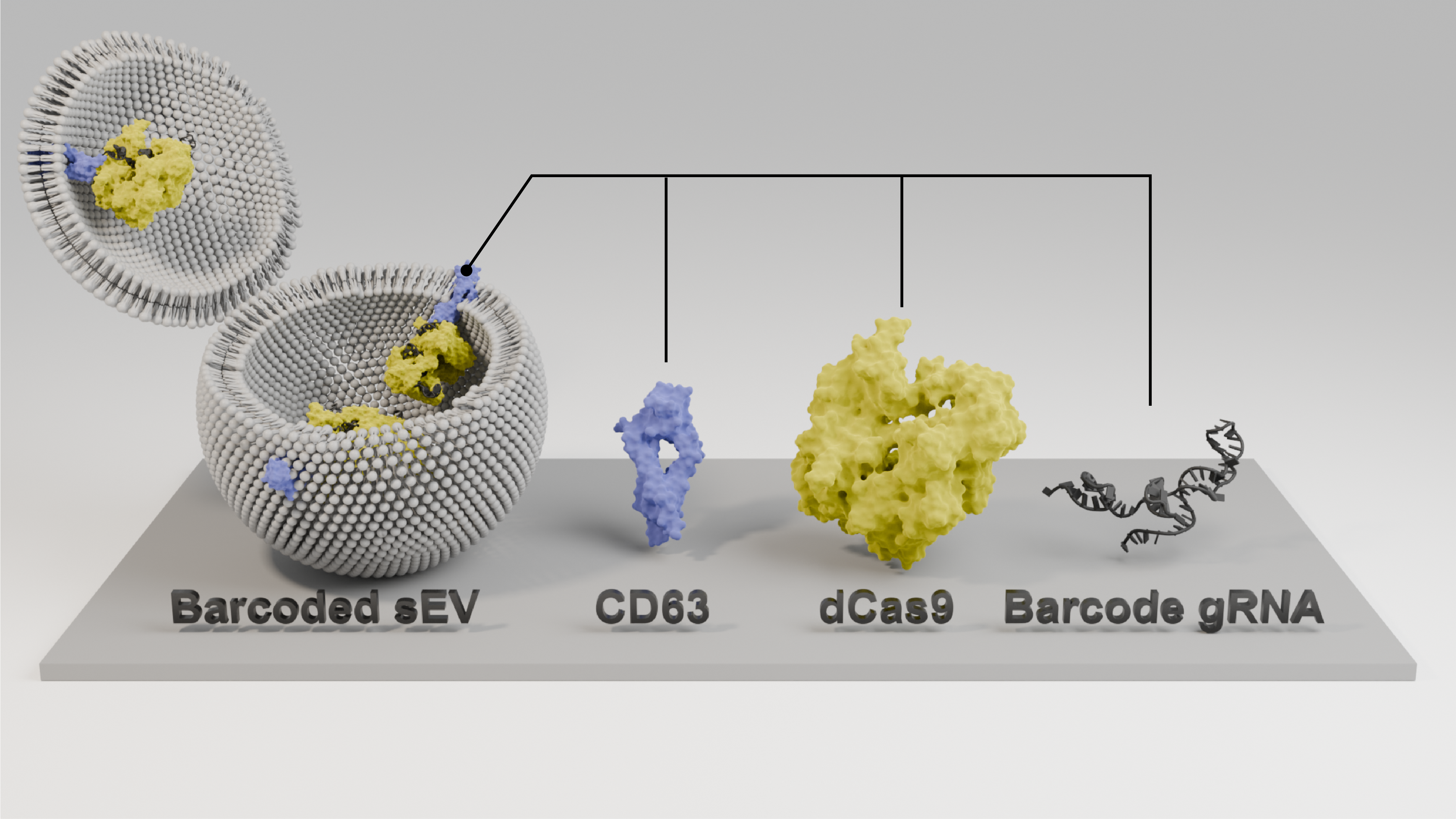
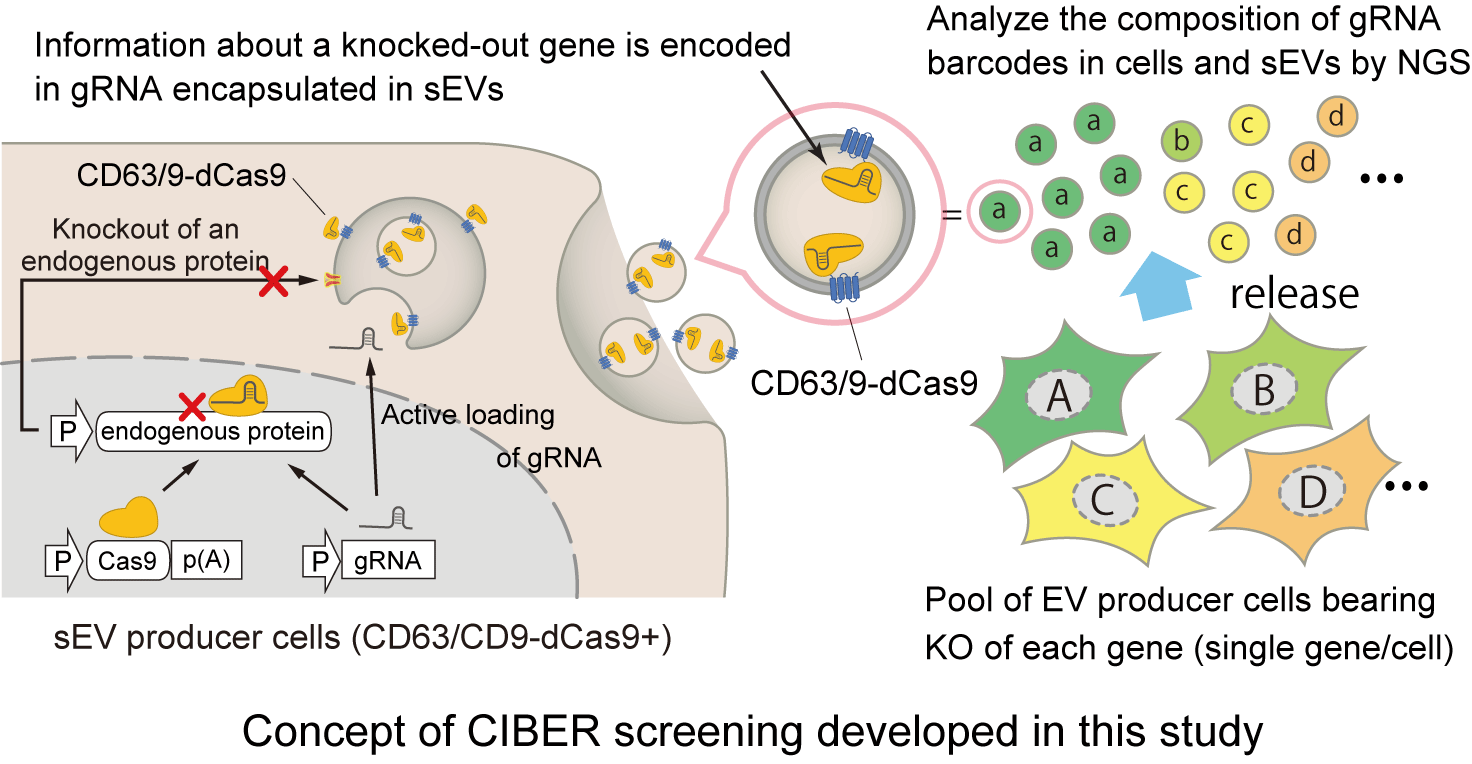
In previous studies, Kojima and team established a system to actively load specific RNA into sEV by using the interaction of an RNA binding protein (RBP) fused with an EV marker protein and an RNA bearing a binding motif against the RBP. In the current study, published in Nature Communications, the researchers conceived to make synergy of the system to load RNA into sEV with the CRIPSR pooled screening system to enable massively parallel identification of sEV regulators. By adopting dead Cas9 (dCas9) as the RBP to fuse with an EV marker, the scientists succeeded in efficiently loading the gRNA used for gene knockout (KO) into a sEV, in a subpopulation-specific manner by choosing the EV marker to fuse with dCas9.
The gRNA loaded in the sEVs can be used as "barcodes" that encode the gene KO of their originating cells, and the quantification of the barcode composition in the sEVs and cells enabled massively parallel analysis of the release regulators of the sEV release processes. This screening pipeline was designated as "CRISPR-assisted individually barcoded sEV-based release regulator (CIBER) screening" and enabled to identify previously unknown sEV release regulators successfully and uncovered the sEV release regulators that act differently on CD63+ and CD9+ sEVs, different release mechanisms of which have been poorly understood. The findings included the exosomal/ectosomal nature of CD63+/CD9+ sEVs, respectively, as well as the synchronization of CD9+ sEV release with the cell cycle.
CIBER screening should provide a basis for detailed studies on the biogenesis, release, and heterogeneity of sEVs, and can be useful for various future exploratory applications from the viewpoint of both basic sEV biology and biotechnological applications.
Ryosuke Kojima was previously an HFSP Fellowship Awardee, which allowed the HFSP researcher to develop synthetic-biology-inspired "EXOtic devices" for the efficient production of sEVs loaded with RNA of interest aiming at creating "designer" sEVs for efficient cargo delivery by engineered sEVs. Through this study, researchers from the University of Tokyo were convinced that the sEVs are promising as therapeutic modalities but acknowledged that a deep understanding of sEV biology was necessary for further exploiting the potential of sEVs for future applications. Based on this understanding, the scientists have established a new exploratory system to unveil the genes/proteins that control the release and fate of the sEVs. Now, supported by an HFSP Career Development Award, the researcher and team have established the CIBER screening system in this study. Ryosuke Kojima affirms, "Without the support of HFSP, it must have been difficult to concentrate on the project for a long term, so we are indeed grateful for their support over a long period!"


































